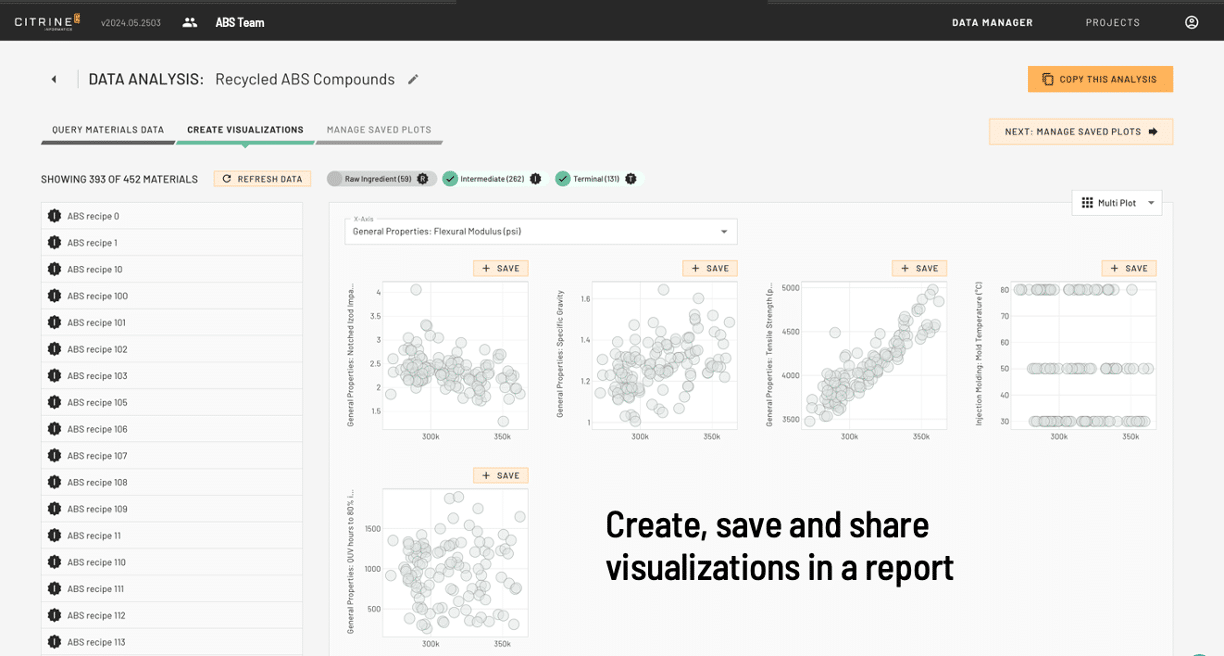
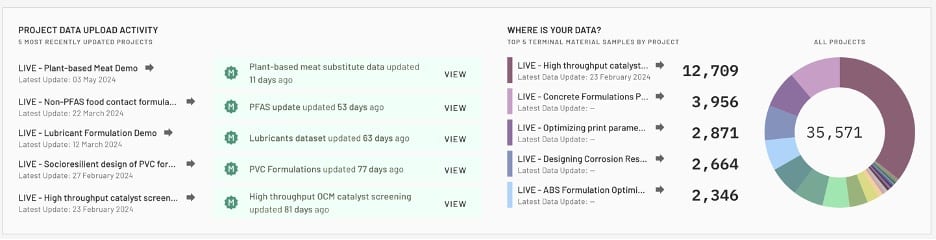
Citrine | DataManager
Scalable data management for chemicals, materials, ingredients and products.
FAQs
-
What types of data are used in materials informatics?
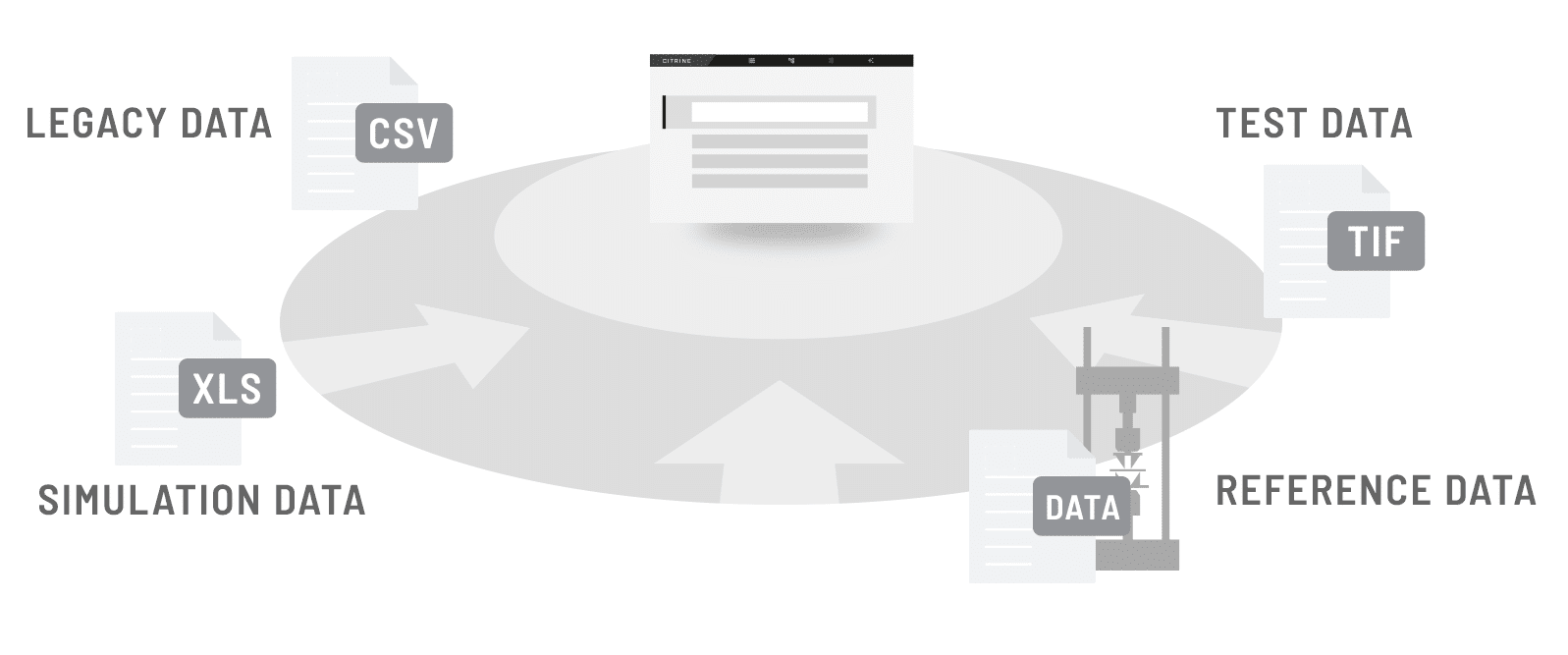
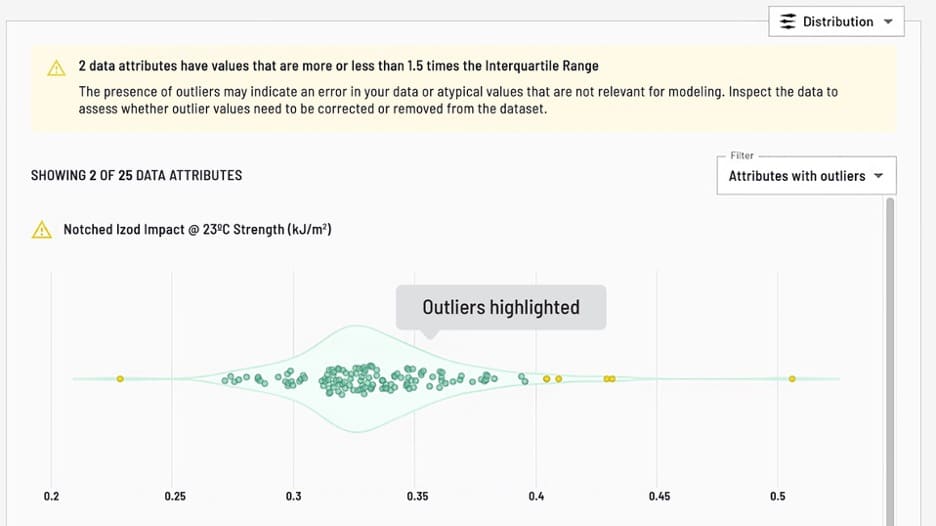
Data used in materials informatics can include experimental measurements, computational simulation results, images (such as micrographs), text (such as research articles and datasheets), and other forms of structured and unstructured data related to materials and chemicals.
-
How much data do you need to get started with AI for materials and chemicals?
While it is true that more data is better, it is more important that the data is diverse, showing failures as well as successes and covering the whole search space. We can start using AI with 12 data points, 30 data points is a solid start, 100 data points is great. (A data point = an experiment (formulation data + processing parameters + final material properties).
-
How does Citrine keep customer data secure?
Citrine Informatics is ISO 270001 accredited. You can read about data security in detail here. In summary, each customer has their own encrypted instance of the platform, and only they can access their data and their models. Data and models are not shared across customers and even Citrine employees need permission from customers to access their data when helping them on projects.
-
How does materials informatics handle the complexity of materials data?
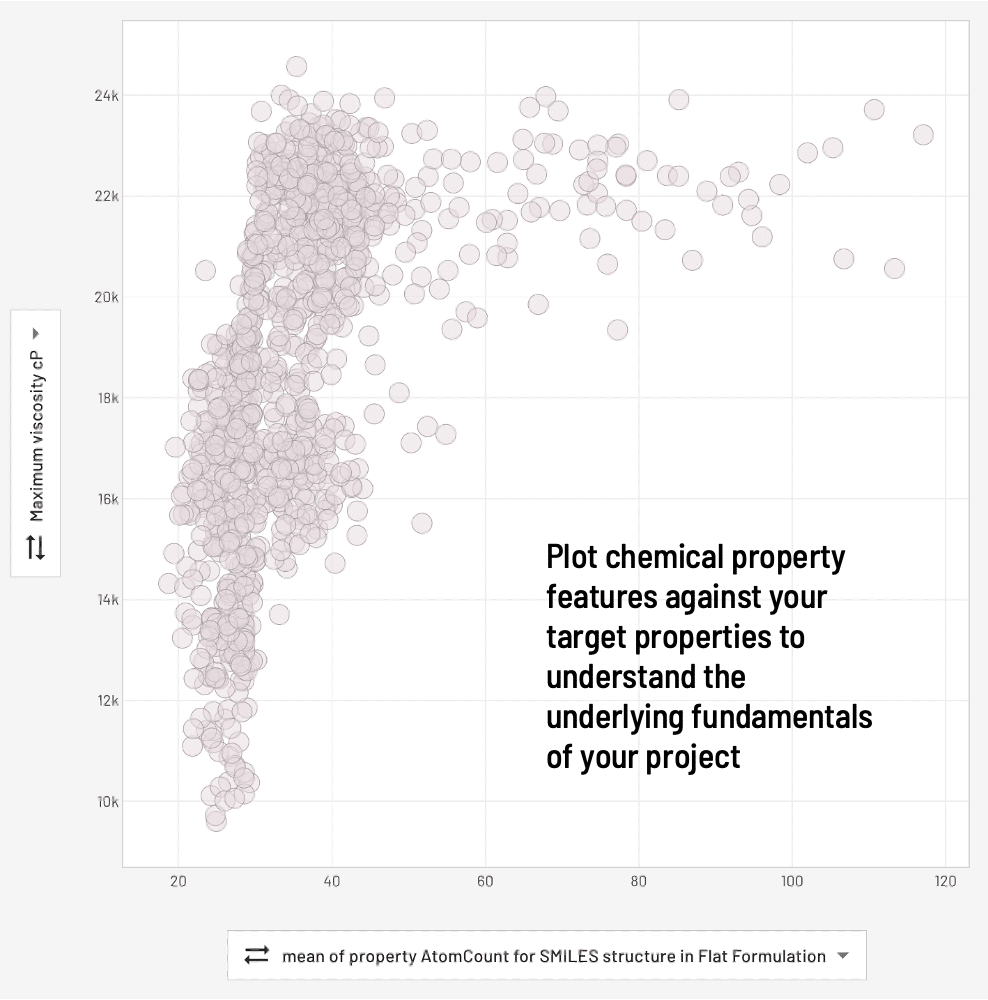
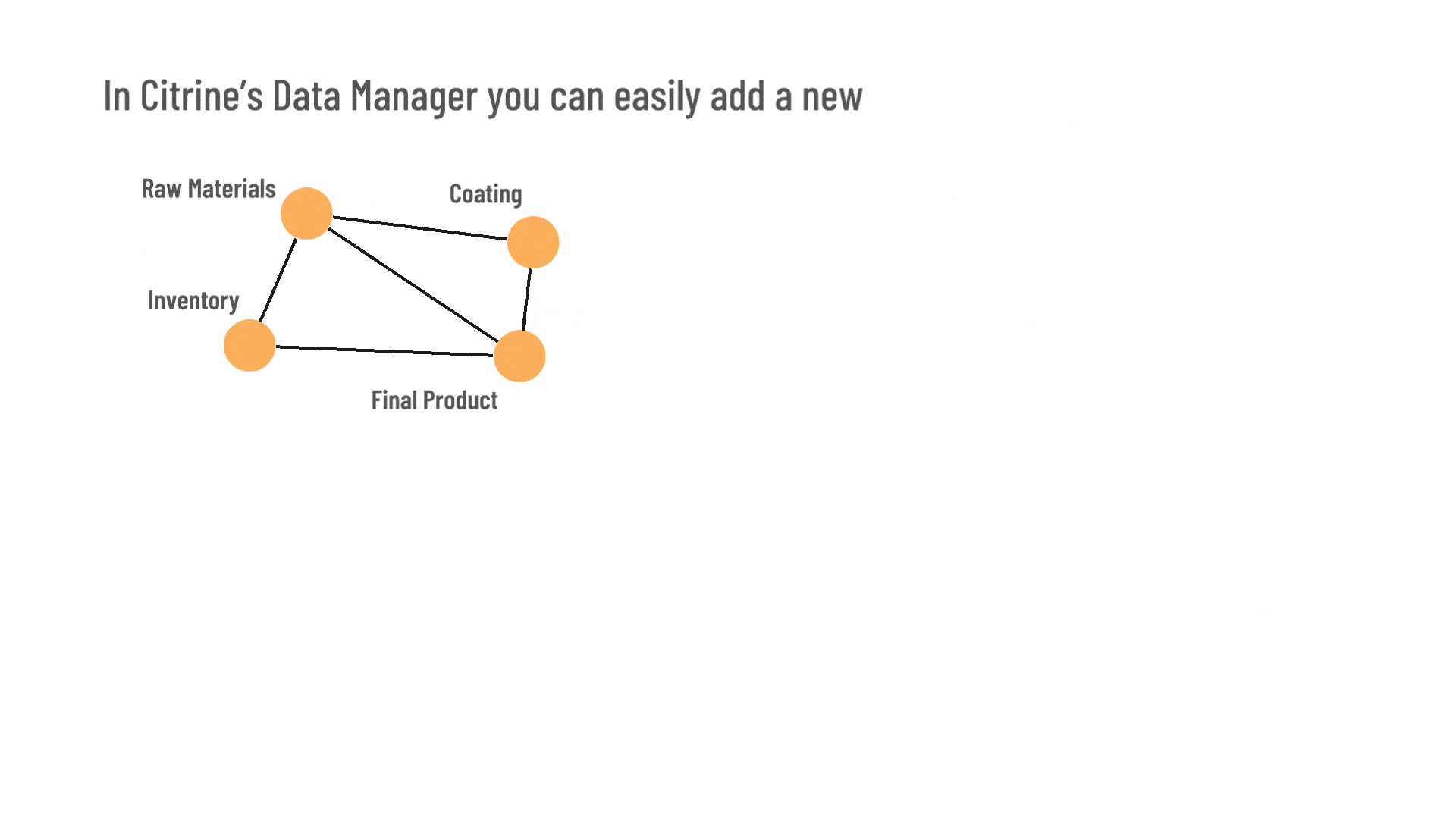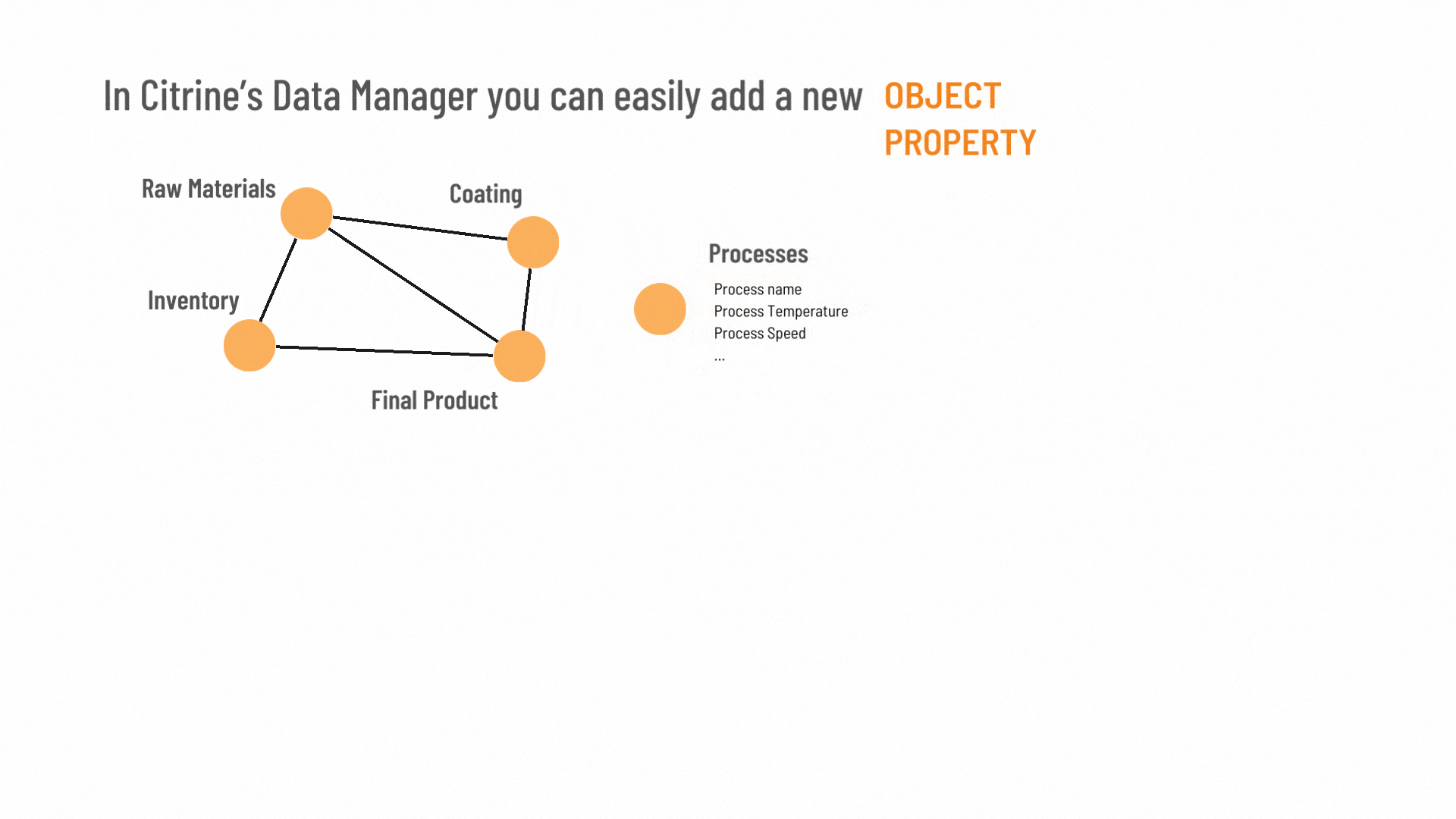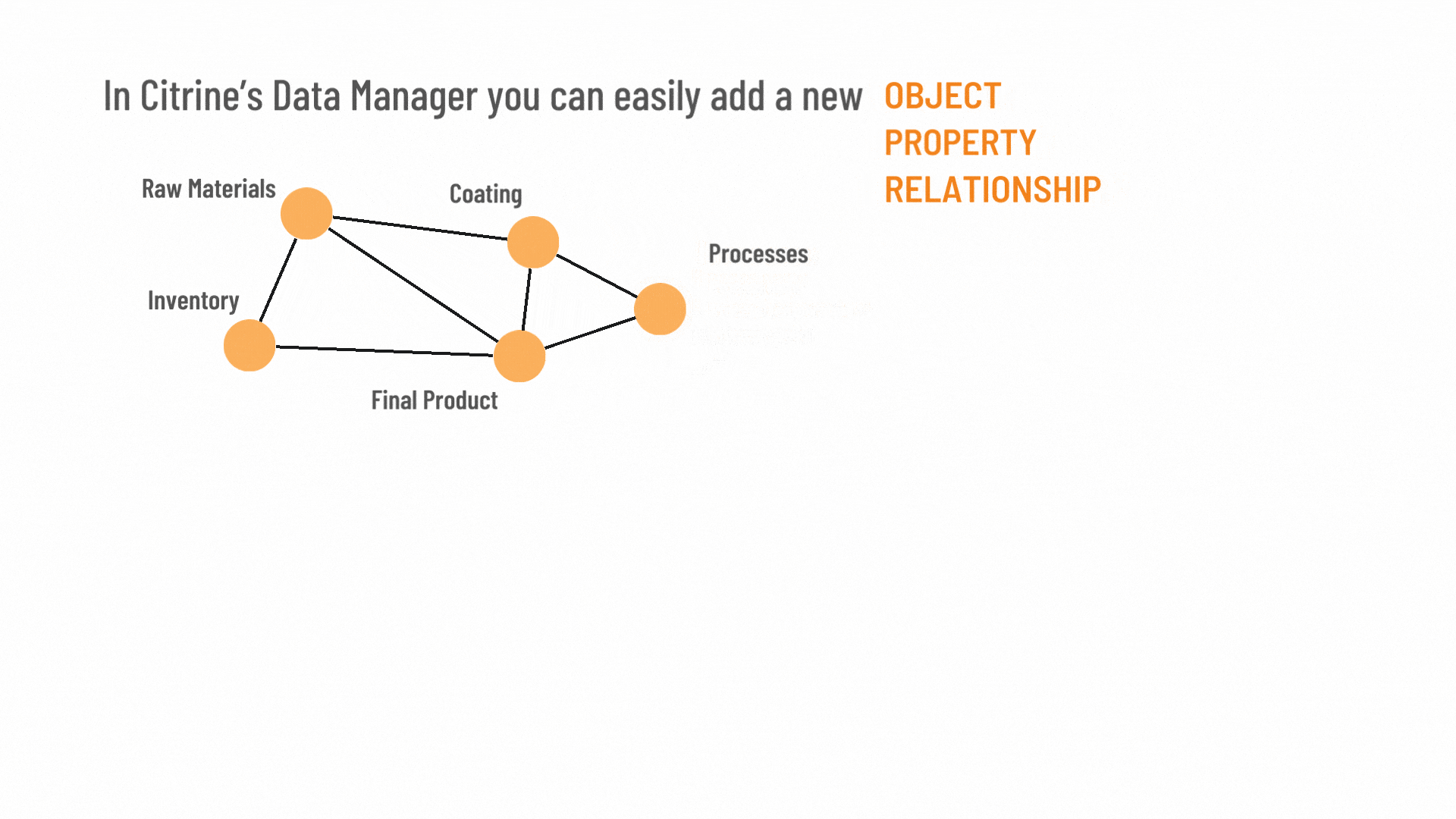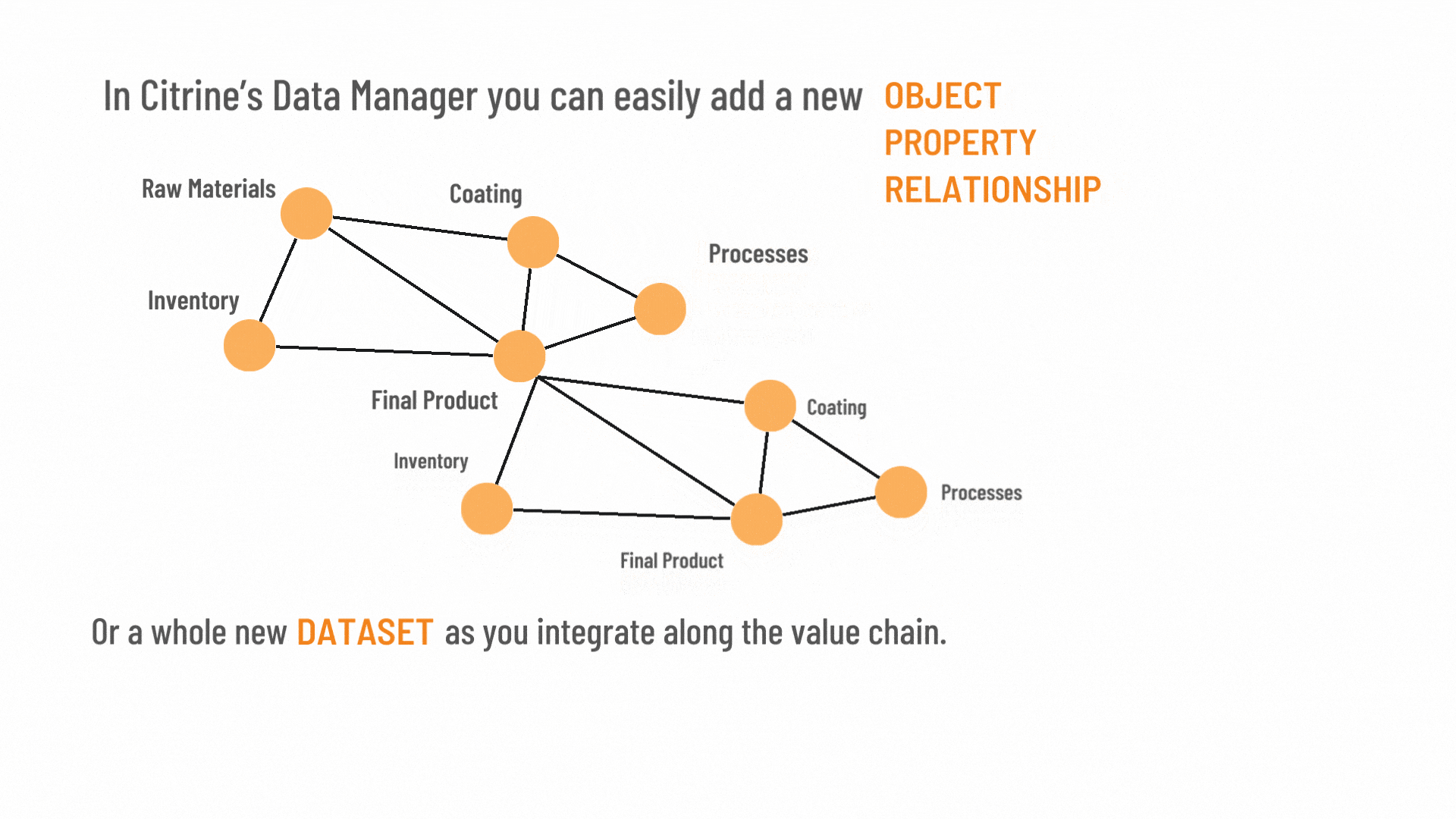
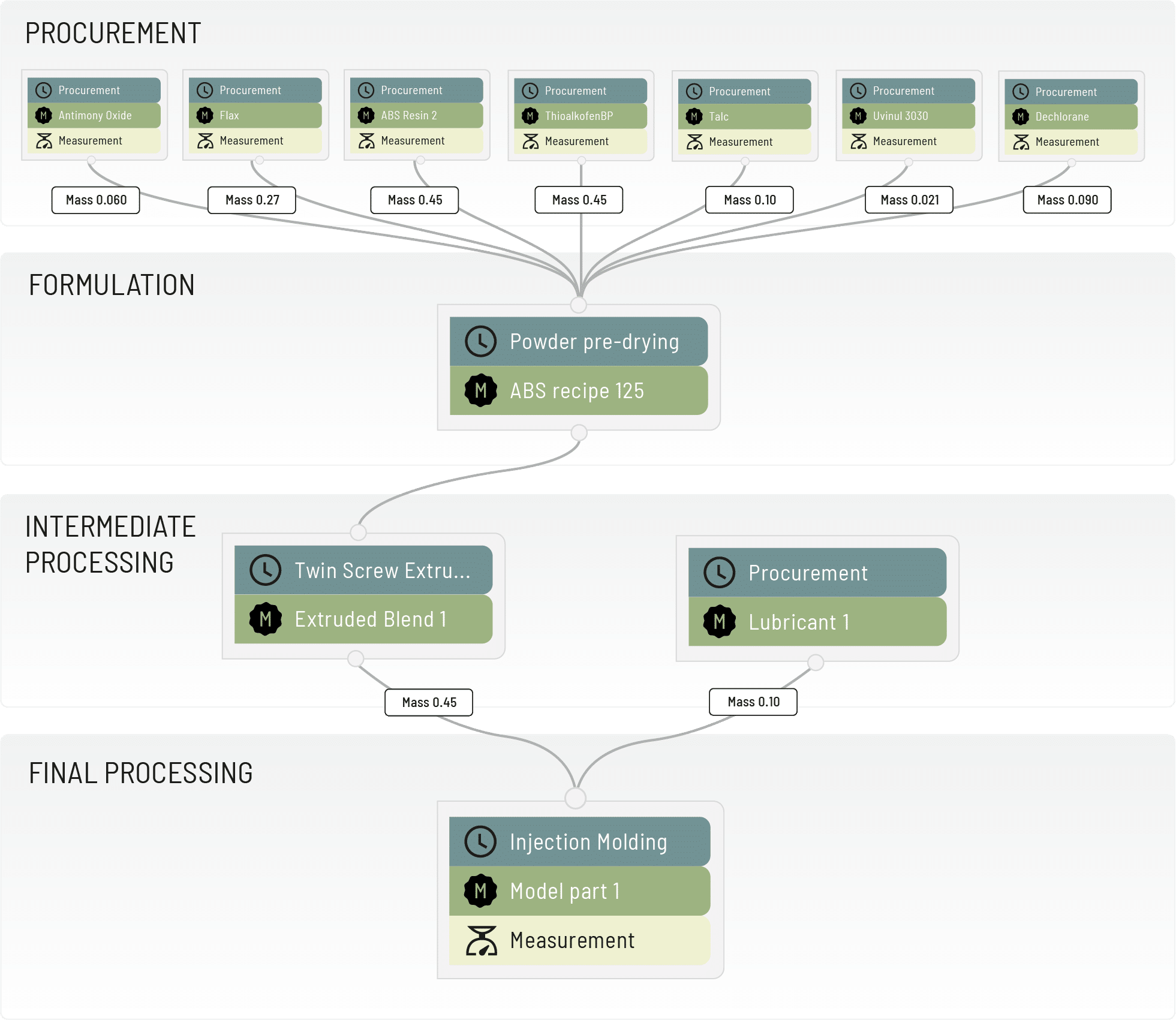
Feature engineering is used to distill complex data into manageable and insightful forms. Feature engineering is the process of deciding which bits of information could be useful to a model in predicting the properties of interest and getting them into a format that maximizes a model’s ability to learn. Domain knowledge is crucial for this process. While many features in materials and chemicals can be generated quite easily by converting molecular structures and chemical formulas into more detailed representations, there are often nuances that are best leveraged by letting domain experts (those that know their process better than anyone) break down what’s actually important. It is also key to have systems that can record all the conditions at play during sample preparation and record process steps and their parameters as well as ingredients and their amounts.
-
What is featurization?
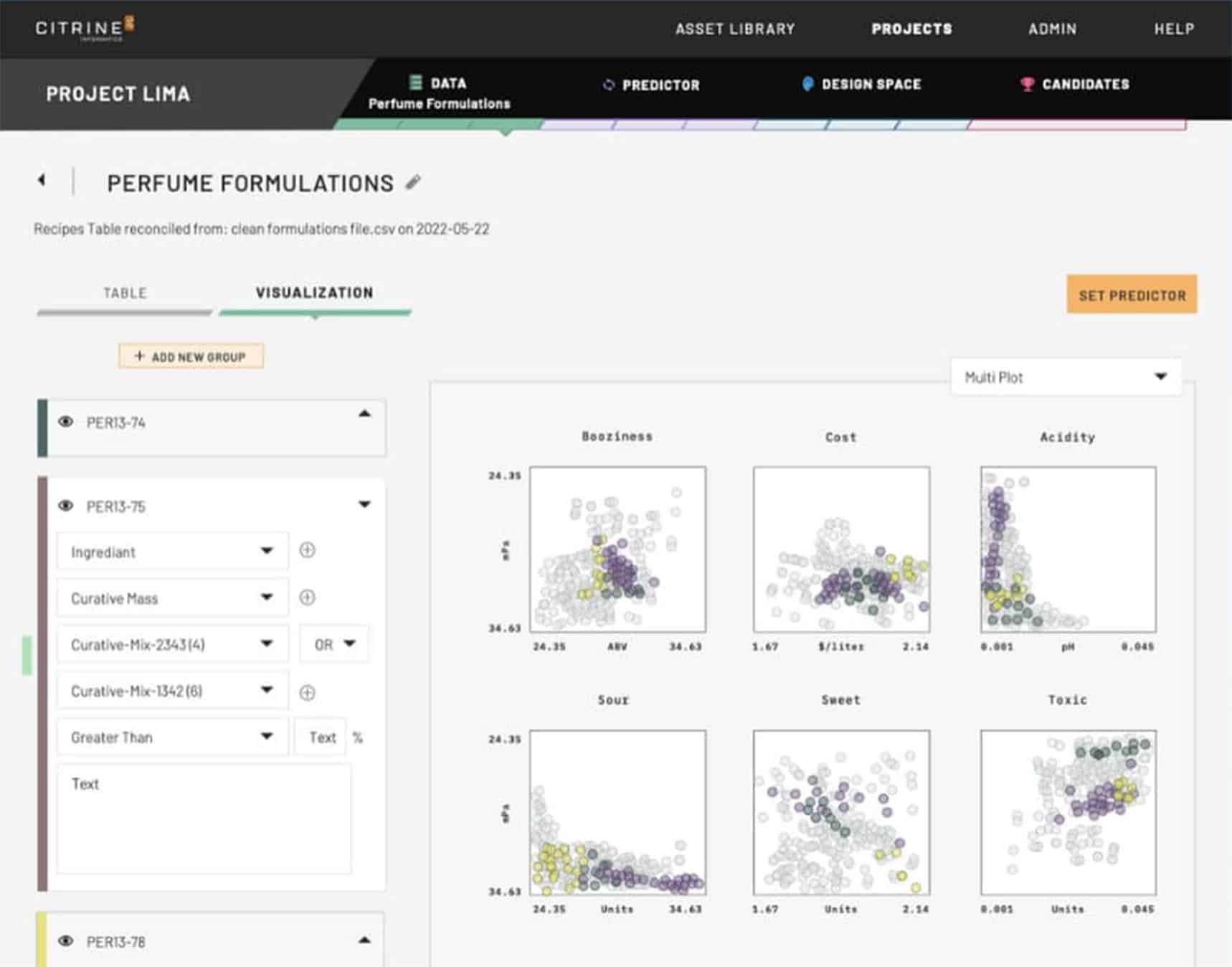
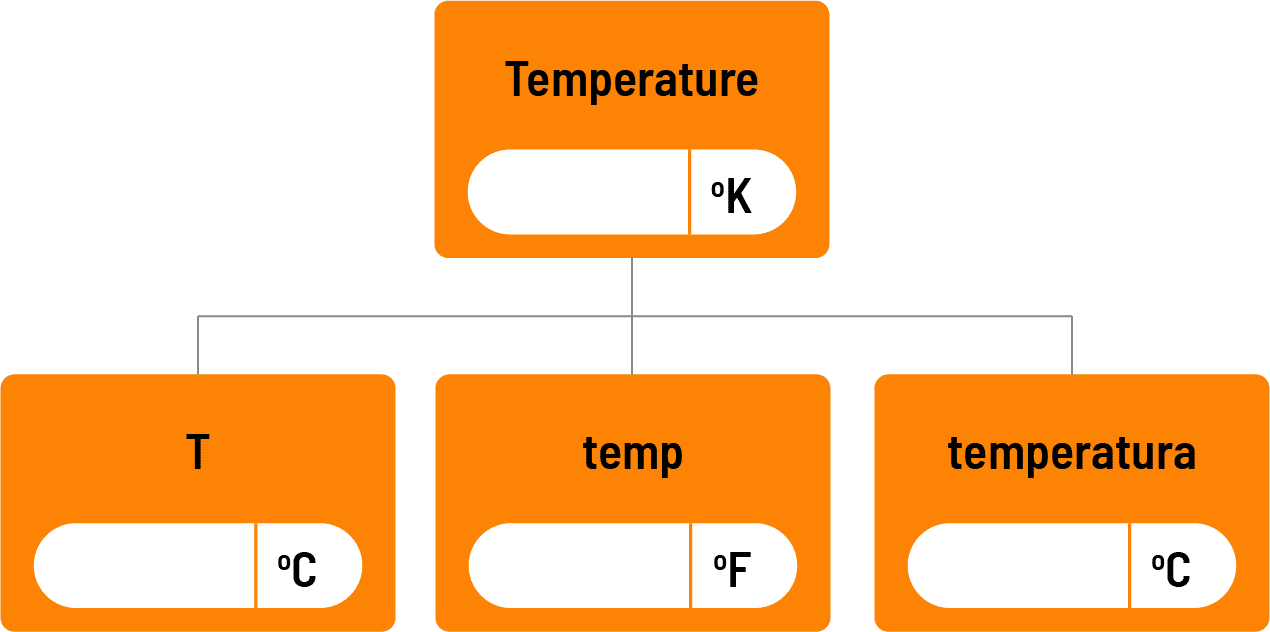
Featurization is the process of transforming raw data into a format that can be used by machine learning models. This involves extracting meaningful features or characteristics from the data that capture the important aspects needed to predict a property of interest. In the context of materials science or chemistry, featurization can involve the process of converting molecular structures into data such as the molecular weight and number of hydrogen bonds, or distilling charts into data representing features such as peak values.
-
What are SMILES and InCHI, and how are they used on the Citrine Platform?
SMILES (Simplified Molecular Input Line Entry System) and InCHI (International Chemical Identifier) are notations used to represent the structure of chemical molecules in text format. It provides a way to encode molecular structures using short ASCII strings, which makes it convenient for inputting chemical information. In the Citrine Platform these are automatically converted into extra data about the molecule to feed into the AI model. For example, if you know the SMILES string you can automatically calculate the number of hydrogen bonds. The platform automatically calculates 127 different features of each molecule that are relevant across different domains. These include surface properties, reactivity, polarizability etc.
-
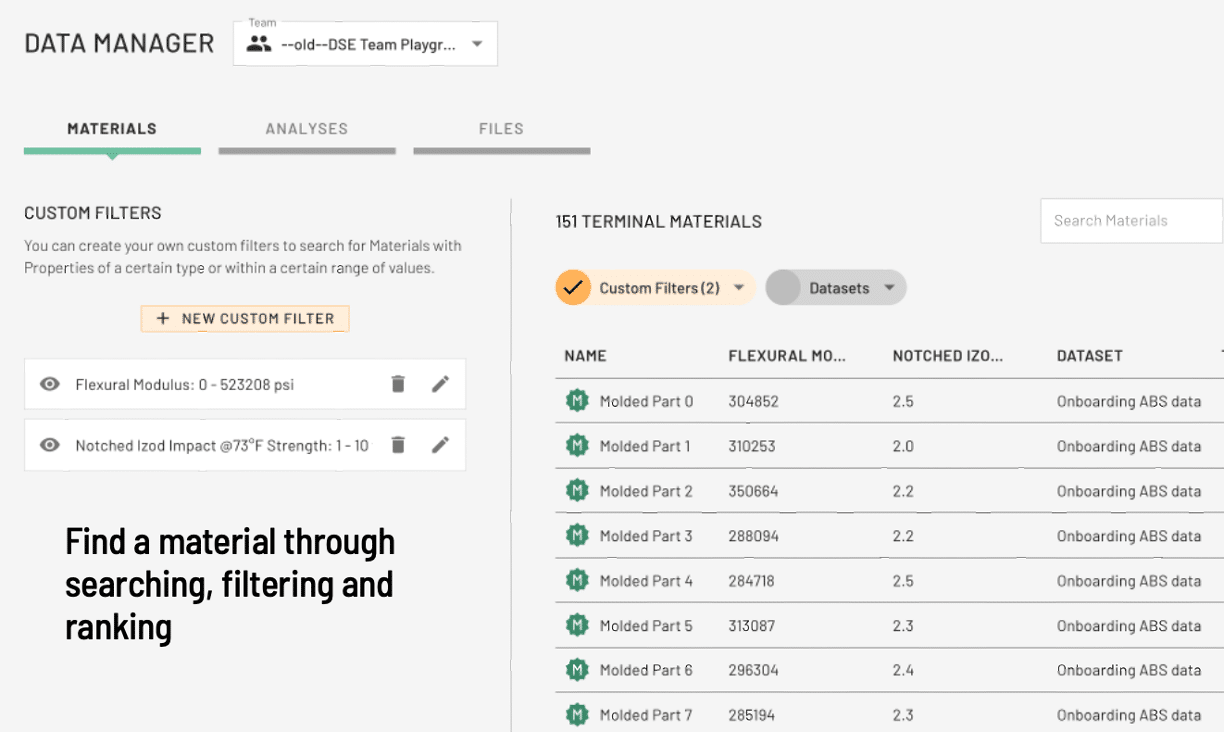
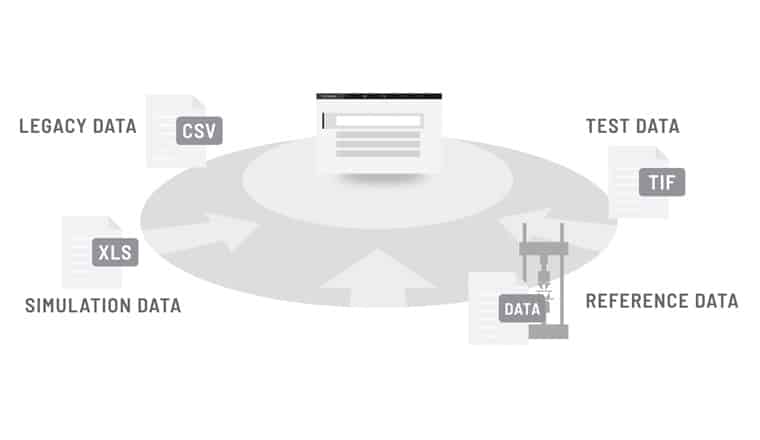
What is data ingestion?
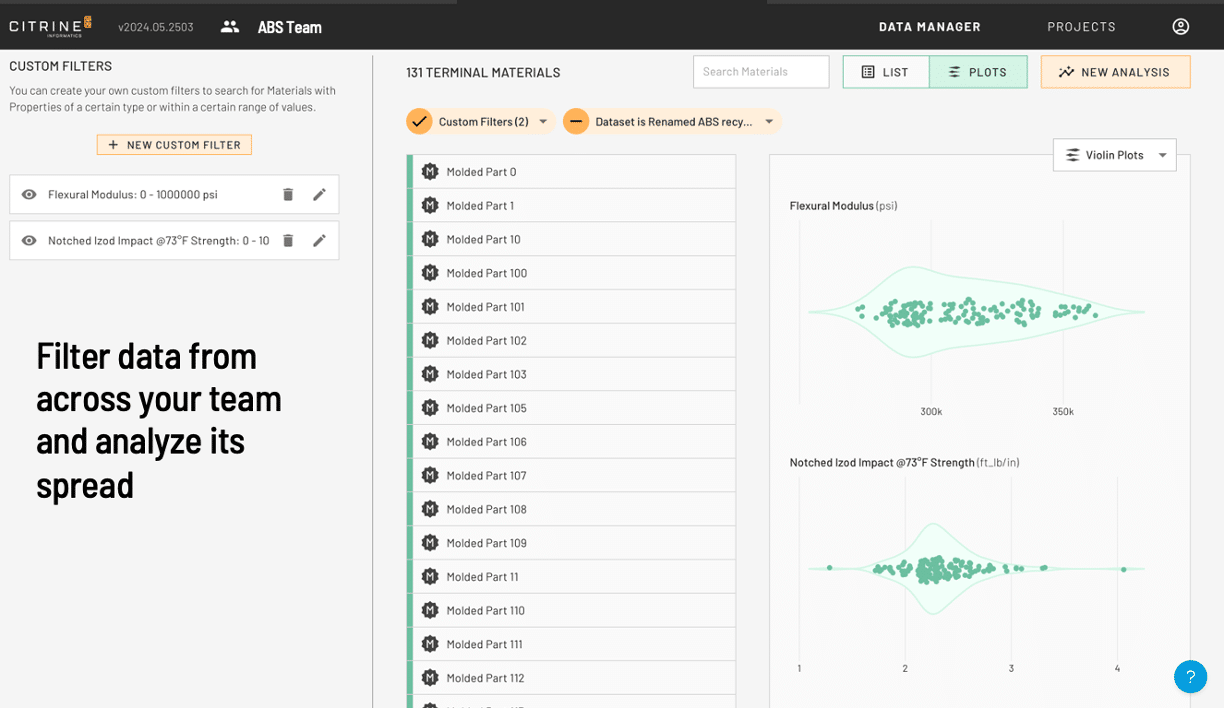
Data ingestion refers to the process of collecting, importing, and processing data for use in a data system or application. In the case of the Citrine Platform this can be done by uploading an excel spreadsheet or by creating data pipelines directly from your data systems.